Please wait...
About This Project
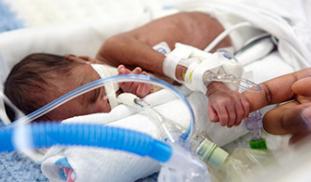
Necrotizing enterocolitis is a severe inflammatory gastrointestinal disease and is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality (30-50%) in preterm neonates. An altered newborn's gut microbiota plays a major role in this condition. We hypothesize that secreted factors from one probiotic, Bifidobacterium infantis, could exert anti-inflammatory effects in the newborn's intestine. These observations might lead to ways to prevent excessive intestinal inflammation causing necrotizing enterocolitis.

Browse Other Projects on Experiment
Related Projects
Shutting down cancer’s recycling system with exosome-based therapy
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers because its cells survive by recycling their own components...
Developing a novel oxysterol antibiotic to combat drug-resistant tuberculosis
Drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) is a consistently growing threat to global health. We have developed Oxy291...
Tote-Size portable incubator for rapid field work
Waiting for lab results is slowing science down! We are designing a fully open source portable incubator...