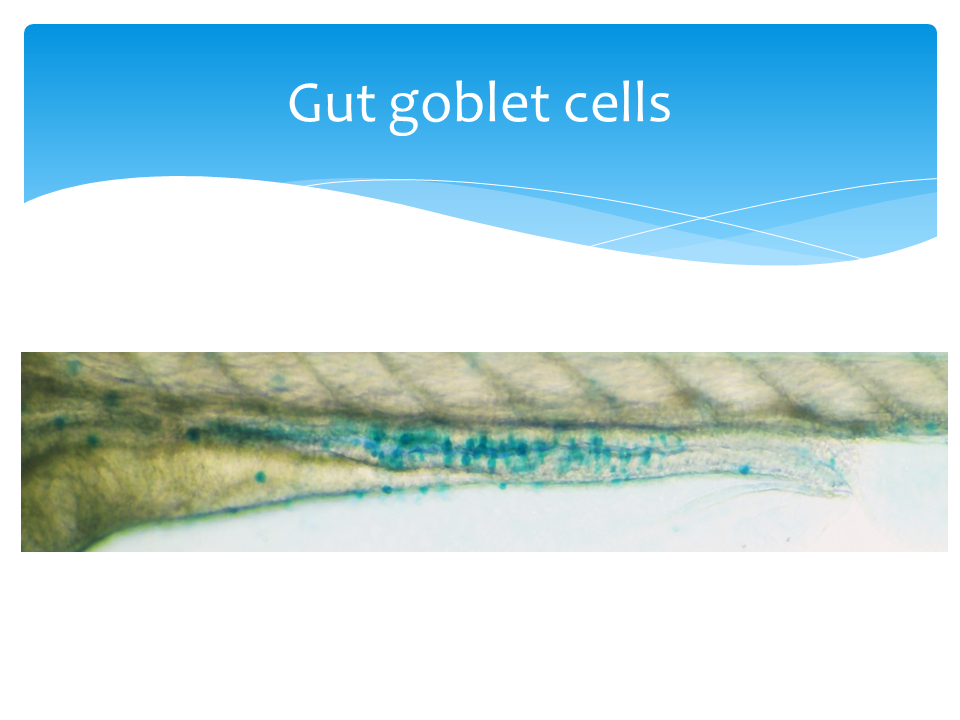
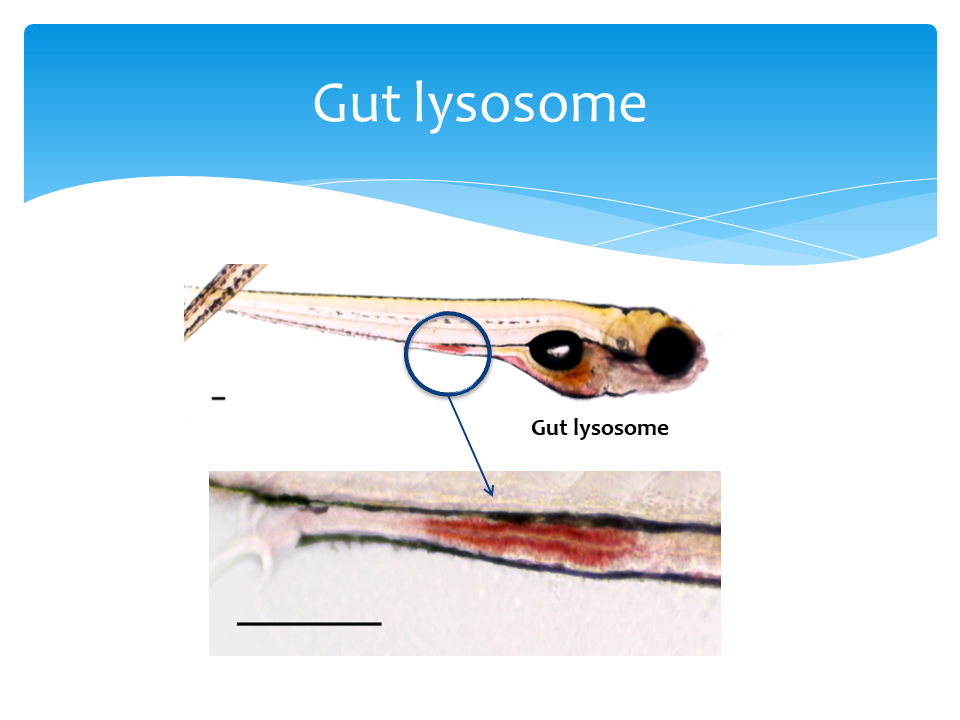
 The neutral red and Alcian blue staining protocols were adapted and optimized from Oehlers et. al. 2013 (PMID:23448252). Zebrafish larvae were staining live with 2.5 μg/ml neutral red (ACROS, Bridgewater, NJ) in egg water for 5 hours. The intensity of neutral red staining is non-saturated and consistent between 4 to 6 hours (S. figure 2a). After move stained larvae to fresh 50 ml egg water, anesthetize larvae in tricaine-S (Western Chemical) and immediately live imaging. For the zebrafish intestinal injury model, mucin was stained as the quantifiable metric. Larvae were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for two hours, rinsed twice with acid alcohol (70% ethanol with 1% hydrochloric acid) and stained in 0.01% alcian blue (w/v, in 80% ethanol with 20% glacial acetic acid) for three hours at room temperature. The alcian blue intensities were linear and non-saturated at two to four hours of staining (S. figure 3a and 3b). After rinsed with acid alcohol three time, fixed larvae were imaged on a thin layer of 0.8% agarose gel.
The neutral red and Alcian blue staining protocols were adapted and optimized from Oehlers et. al. 2013 (PMID:23448252). Zebrafish larvae were staining live with 2.5 μg/ml neutral red (ACROS, Bridgewater, NJ) in egg water for 5 hours. The intensity of neutral red staining is non-saturated and consistent between 4 to 6 hours (S. figure 2a). After move stained larvae to fresh 50 ml egg water, anesthetize larvae in tricaine-S (Western Chemical) and immediately live imaging. For the zebrafish intestinal injury model, mucin was stained as the quantifiable metric. Larvae were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for two hours, rinsed twice with acid alcohol (70% ethanol with 1% hydrochloric acid) and stained in 0.01% alcian blue (w/v, in 80% ethanol with 20% glacial acetic acid) for three hours at room temperature. The alcian blue intensities were linear and non-saturated at two to four hours of staining (S. figure 3a and 3b). After rinsed with acid alcohol three time, fixed larvae were imaged on a thin layer of 0.8% agarose gel.
For both neutral red and alcian blue staining, the images of full gut and/or lumen were collected under 100x total magnification with the EVOS XL core microscope (Thermo fisher Scientific). Using ImageJ software, we inverted the color of the image, traced the gut and/or lumen, and measured the mean intensity per pixel. To remove background noise, we subtracted the mean intensity per pixel of images from anal end of the gut as background in fish. The relative expressions (%) were calculated by normalizing to the untreated group. Statistical tests were done with Wilcoxon-test in R studio.