Methods
Summary
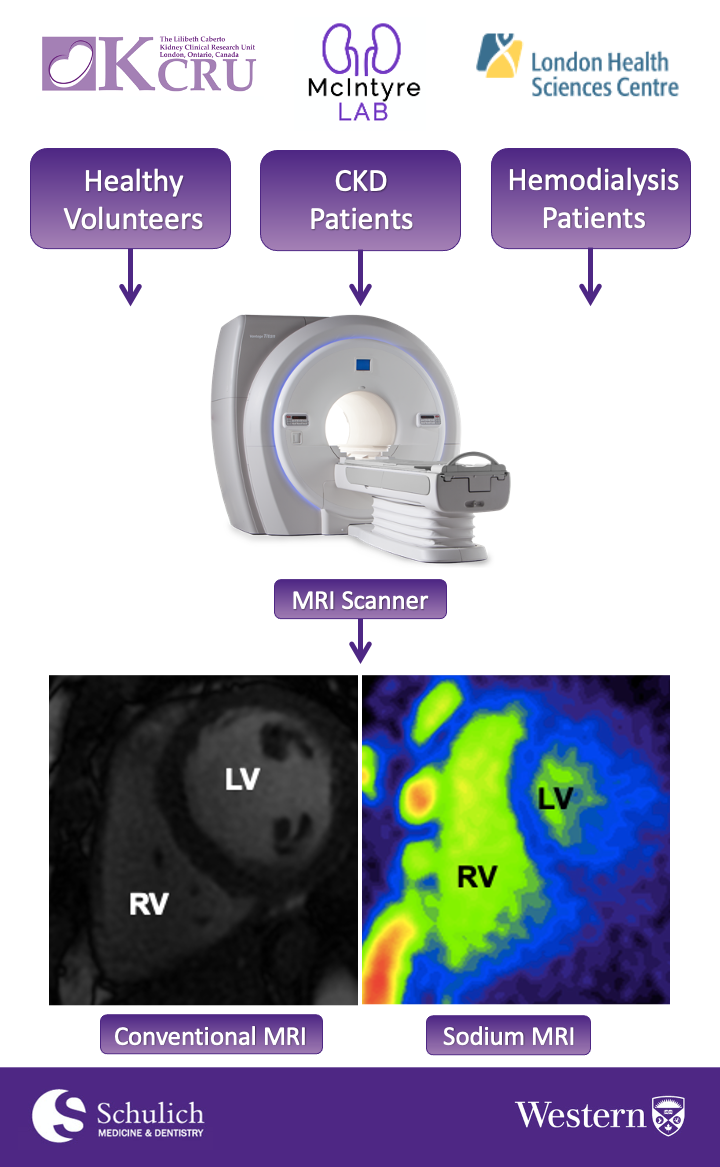
For this study, we will be recruiting up to 150 participants; approximately 50 hemodialysis patients, 50 patients with various stages of chronic kidney disease, and 50 individuals with no kidney disease. Once recruited, participants will undergo one study visit (on a non-dialysis day for hemodialysis patients). Before imaging, the participants will have their weight recorded, have their blood pressure taken, provide a heart rate measurement, and provide a blood and urine sample. Each participant will then be imaged using a 3T MRI scanner to acquire a proton and sodium MRI scan of their heart.
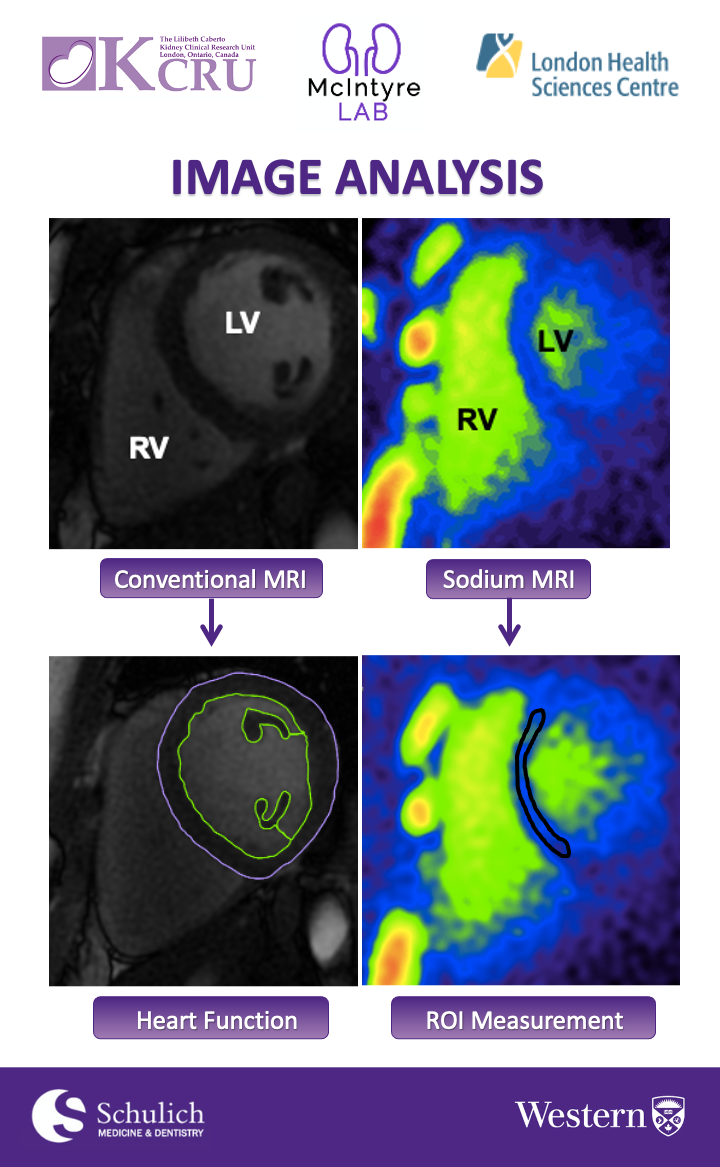
Once the images are acquired, they will be analyzed. We will be using image analysis software to draw contours around the different regions of the heart in the proton MR images to assess the cardiac function of each participant. We will then be using the software to draw regions of interest around the septal region of the heart in the sodium images to measure the sodium signal in each participant's heart tissue. Lastly, we will be comparing heart tissue sodium signals between each of the participants and correlating them with the cardiac function analysis to determine whether salt build-up is a potential cause of heart disease in these kidney disease patients.
Protocols
This project has not yet shared any protocols.