Methods
Summary
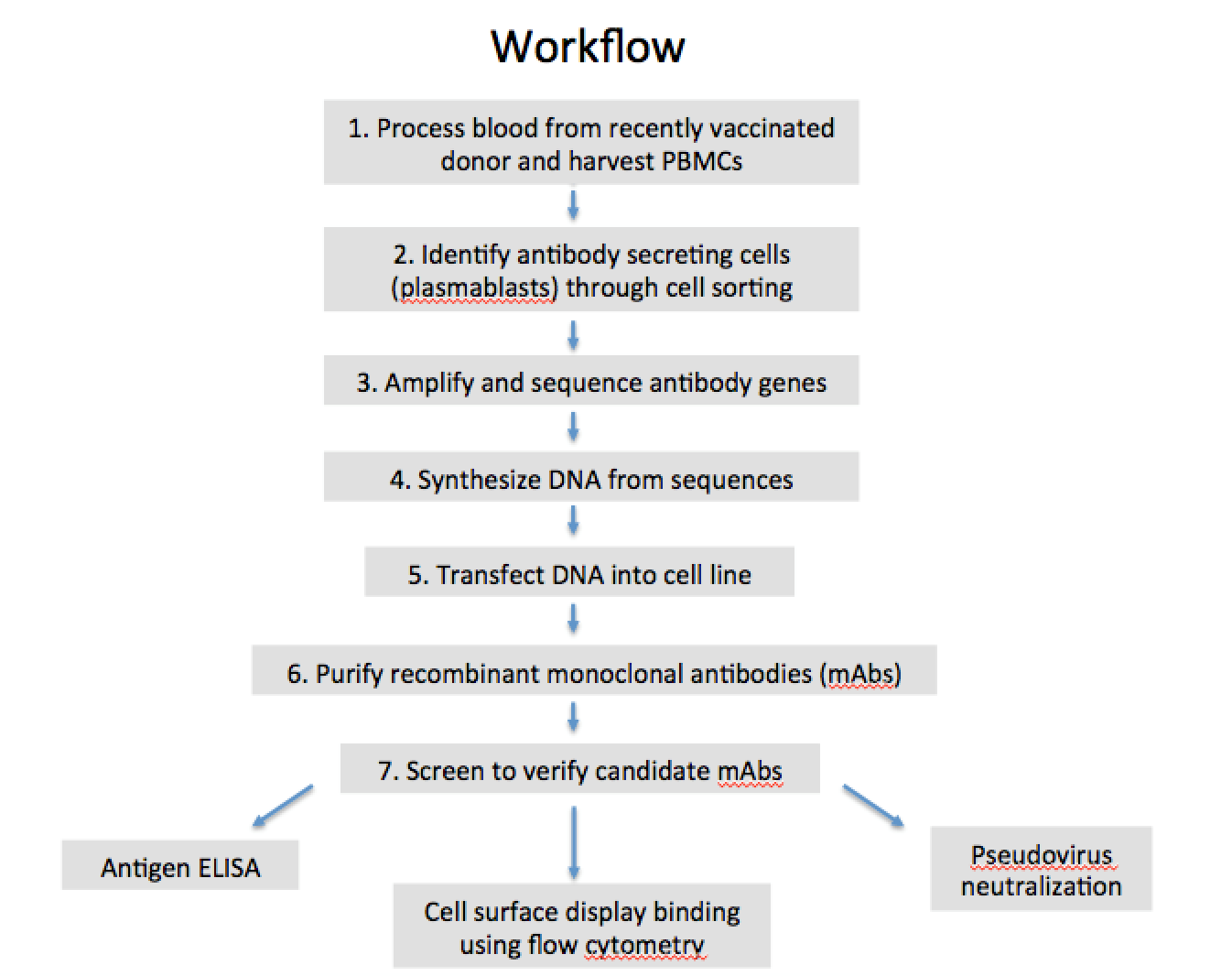
We have blood from a human donor who received three doses of rabies vaccine and donated blood at several time points shortly after vaccination. After we process the blood to isolate PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells), we will identify the antibody-secreting plasmablasts (immature B cells activated as a result of vaccination) through a flow cytometry single cell sorting approach. We then will sequence the antibody genes present on these plasmablast cells to determine the likely candidates for rabies specific antibody. We will synthesize the DNA to validate the sequences, and will transfect it into a cell line in order to make the antibodies recombinantly. Finally, we will test the recombinant antibodies for binding to viral protein through ELISA and flow cytometry, and will test for virus killing using pseudoviruses (viruses that are safer to work with than the real rabies virus).
Protocols
This project has not yet shared any protocols.